Loratadine: What Is It For And What Are Its Contraindications?
Loratadine is a drug that interacts with histamine H1 receptors. More specifically, it competes with histamine for union with this type of receptor.
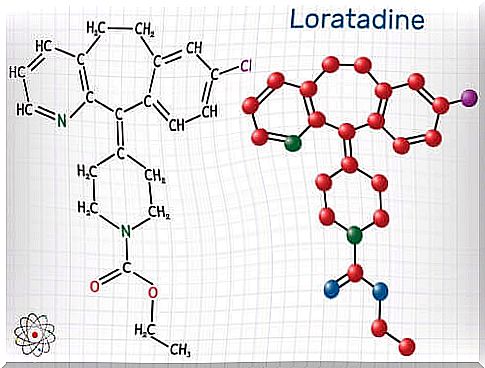
Loratadine is an active H-1 antihistamine drug that is used to treat allergy symptoms. It is administered orally.
Unlike other antihistamine drugs, such as astemizole or terfenadine, loratadine does not produce sedation. This is explained by its poor penetration into the central nervous system and by the fact that it has a low affinity towards the H-1 receptors in this part of the body. It is also not associated with torsades de pointes, which are ventricular tachycardias.
This antihistamine usually combines with another medicine, pseudoephedrine, which is a decongestant, useful for colds and to reduce allergic symptoms.
Thus, loratadine (also known as claritin ) is indicated to relieve symptoms of chronic urticaria and other allergic skin conditions. Besides, it works for the treatment and control of symptoms of allergic rhinitis like sneezing, rhinorrhea and itching.
It also relieves allergic conjunctivitis and its symptoms, such as tearing and burning in the eyes.
How are allergic symptoms triggered?

Allergy is an increased reaction of the body to particles or substances that are harmless to most proteins. The substances to which one is allergic are called allergens. Symptoms are defined as “allergic reactions”.
When an allergen enters the body of a person who is allergic to it, the immune system, which is made up of the body’s innate defenses, responds by producing numerous antibodies to the substance.
Antibodies are protein molecules that are responsible for fighting the foreign substance that has entered the body.
Successive exposure to the same allergen will cause that antibody to trigger a release of chemical mediators which will cause the typical symptoms of the allergic reaction.
Among these symptoms, we can find:
- Skin: reddening, inflammation, itching, rash.
- In the eyes and ears: itchy, red eyes and tearing.
- In the respiratory tract: sneezing, coughing and itchy throat.
- Digestive: lesions on the skin, respiratory and vomiting.
Mechanism of action: how does loratadine affect the body?
As we said, loratadine is a drug that interacts with histamine H1 receptors. More specifically, it competes with histamine for union with this type of receptor.
This is a competitive antagonism that prevents histamine from sticking to its receptor and blocks the effects of loratadine on receptors in the digestive tract, uterus, large vessels and bronchial muscles.
H1 blockers have a series of properties that they share with anticholinergics, antispasmodics, and lymph node and adrenergic blockers.
Loratadine is, however, virtually devoid of anticholinergic effects, and in vitro studies have shown that this drug has only a low affinity for cholinergic and alpha-adrenergic receptors.
Contraindications to the use of loratadine
This medication is contraindicated in people with known hypersensitivity to it. The small anticholinergic activity of H1 antihistamines can thicken the bronchial secretions.
Also, acute asthma attacks can get worse. However, this anticholinergic activity does not exclude the use of antihistamines in asthma patients, especially when drugs such as loratadine with a very weak anticholinergic component are used.

In addition, loratadine may produce lethargy and drowsiness in some patients. It is therefore essential to inform this type of patient of the dangers of driving or using dangerous machines if they are treated with this medication.
Furthermore, it should also be taken into account that, in children under 2 years of age, the safety and efficacy of this drug have not yet been established. It should therefore not be used in this population group.
Women who are breastfeeding and being treated with loratadine should avoid its consumption. Indeed, it is excreted in part through breast milk.
Loratadine is a widely used drug
Loratadine is a drug widely used to combat allergic symptoms. Its effectiveness is due to its ability to interact with histamine H1 receptors. It thus avoids the union of histamine with the latter.
It has the advantage of not producing sedation in patients who consume it. However, it is contraindicated in a number of situations because of the complications it tends to trigger.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have any doubts about loratadine treatment, and be sure to report any symptoms you may have after treatment.